How IV Therapy Helps Brain Injury Patients
Traumatic brain injuries are a public health problem. Because the brain is such a complex and delicate organ, deciding on the right treatment plan for a traumatic brain injury can be overwhelming. However, emerging medical solutions, such as IV therapy, may make invasive brain surgery more of a last resort.
To help you better understand brain injury procedures, this article will review what qualifies as a traumatic brain injury and how IV therapy benefits brain injury patients by explaining the finer details of IV therapy, including its common uses and risks. If you or a loved one may have sustained a traumatic brain injury, keep reading to find out more about potential treatment options.
Explore Brain Injury Rehabilitation Offered by PAM Health

What Is a Traumatic Brain Injury?
A traumatic brain injury typically occurs from a violent blow to the head or body and impacts the brain's ability to function. A mild traumatic brain injury may temporarily affect the brain cells, whereas a more significant traumatic brain injury could result in torn brain tissue, bleeding, bruising and other damage. A severe traumatic brain injury could lead to long-term complications or death.
A traumatic brain injury can come with a wide range of physical and psychological side effects. These symptoms may become apparent immediately following the traumatic event or emerge days or even weeks later.
To spot a brain injury and treat it as early as possible, look for these physical signs and symptoms.
- Loss of consciousness: A mild brain injury includes loss of consciousness for a few minutes, while a more severe one could involve loss of consciousness for hours or even a coma and other disorders.
- Headaches: A more severe brain injury will usually come with repeated or worsening headaches.
- Disorientation: Mild brain injuries often involve a state of disorientation or confusion. A moderate traumatic brain injury may include dilated pupils, convulsions or seizures.
- Drowsiness or fatigue: Those with mild brain injuries may sleep more than usual, while moderate traumatic brain injury patients may experience an inability to wake from sleep.
- Dizziness: A severe brain injury could include loss of coordination and weakness or numbness in the fingers and toes.
- Nausea or vomiting: Those with a moderate traumatic brain injury might also experience clear fluids draining from their ears or nose.
In addition to physical signs, keep an eye on these mental or cognitive symptoms.
- Sensory issues: Brain injuries typically include sensory problems like blurred vision, sensitivity to light or sound, ringing in the ears or an inability to smell normally.
- Memory loss: Mild brain injuries may involve memory or concentration problems, while a moderate to severe brain injury can lead to profound confusion.
- Speech problems: A more severe brain injury is likely to include slurred speech.
- Mood changes: A mild traumatic brain injury can come with mood swings and feelings of depression or anxiety, while a moderate brain injury often includes agitation, combativeness and other unusual behaviors, too.
The severity of symptoms from a traumatic brain injury usually depends on several factors, including the cause of the injury and the force of initial impact. The most common causes of a traumatic brain injury include the following.
- Falling: Falls are the leading cause of traumatic brain injury. A fall from a ladder, down the stairs, on a patch of ice, in the bath or anywhere else is hazardous for young children and older adults.
- Violence: Another common cause of traumatic brain injury is violence in the form of a gunshot wound, child abuse, domestic violence or another form of assault.
- Vehicle collisions: Accidents involving cars, bikes or motorcycles are often the cause of a traumatic brain injury.
- Sports injuries: Many high-impact sports, such as football, soccer, boxing and hockey, can cause traumatic brain injuries, especially for younger players.
- Military injuries: Explosive blasts and other combat injuries are frequently the cause of traumatic brain injury for active-duty military personnel.
Properly addressing a traumatic brain injury as soon as possible is crucial for preventing further complications. If left untreated, a traumatic brain injury could result in one or more of the following conditions.
- Altered consciousness: A severe traumatic brain injury could lead to prolonged or permanent consciousness changes, such as a coma or vegetative state.
- Physical complications: Those with a severe traumatic brain injury could develop fluid buildup in the brain, seizures, blood vessel damage, facial paralysis and other long-term health effects.
- Intellectual issues: A traumatic brain injury's lasting effects could include cognitive problems like memory, reasoning or concentration struggles, plus problems multitasking, decision-making or completing some tasks.
- Communication challenges: The communication problems that accompany a traumatic brain injury may include difficulty speaking, writing or understanding others.
- Behavioral changes: A traumatic brain injury patient may experience uncharacteristic mood swings and other emotional shifts that lead to risky behavior, outbursts or a general lack of self-awareness.

What Is IV Therapy?
Commonly referred to as IV therapy, intravenous therapy involves using an injection connected to a small tube to deliver fluids directly to the body's veins. Because the method drips nutrients straight into the veins, IV therapy is the fastest way to get medications, blood products, vitamins and other necessities into the bloodstream.
IV therapy is a fast and effective medical technique because it gets essential vitamins and nutrients into the body systems without waiting for the digestive system to absorb them. The stomach and digestive tract must break down a vitamin or supplement taken orally, limiting nutrient absorption by about 50%.
However, when the body undergoes IV drip therapy, it receives a higher vitamin concentration because the bloodstream absorbs it at a much higher rate of about 90%. This absorption efficiency and quickness can help improve various health conditions, blood transfusions and dehydration.
Variables such as age, genetics, health status, metabolism and any other products a patient may consume can also affect their body's ability to absorb vitamins and nutrients in the stomach. Delivering essential nutrients via IV therapy can help raise the levels of vitamins and minerals in the bloodstream, resulting in a greater uptake into the cells, which will use those nutrients to fight off illness and maintain overall health.
During an IV therapy treatment session, a qualified nurse or medical professional will first identify a suitable vein, then inject the needle and secure it into place. The health care provider will then oversee the infusion process and monitor the IV to ensure correct administration of the medication. In total, IV therapy typically takes somewhere between 20 minutes and an hour.
Types of IV Therapy
What is IV therapy used for? IV therapy satisfies a wide range of objectives, from administering life-saving medications to enhancing beauty. Depending on what fluids and other ingredients are in an IV therapy package, the treatment could serve as a nutritional supplement for health or cosmetic purposes.
Here are the four primary uses of IV therapy.
- Fluid delivery: Because IV therapy quickly gets fluids to the body's circulatory system, it is an effective treatment for anyone who is dehydrated, getting sick or feeling run down in general.
- Blood transfusions: An IV can deliver blood during transfusions to replace a large amount of blood loss. Some treatments, such as specific cancers, may require regular blood transfusions, known as transfusion therapy.
- Administering medications: IV therapy can also deliver medicines to the bloodstream, including chemotherapy drugs, some antibiotics and pain medications like morphine.
- Nutrition: An IV therapy package can include crucial vitamins and minerals to strengthen the body's systems and improve overall health. IV therapy treatments often deliver some combination of immune-boosting nutrients like vitamin C, vitamin B12, calcium, magnesium or glutathione, which is a powerful antioxidant.
IV therapy for nutrition is beneficial for traumatic brain injury patients because it is imperative to have stable levels of fluids and established levels of essential vitamins and nutrients before undergoing surgery. The following section will discuss how IV therapy treatment can benefit those with a brain injury.
IV Therapy for Brain Injury Patients
Knowing the various supportive therapeutic techniques for addressing brain injuries is critical for obtaining optimal care. Immediately infusing large amounts of essential fluids to restore blood volume and blood pressure to a stable level is standard procedure for traumatic brain injury patients, which is a goal IV therapy can help achieve.
IV therapy packages filled with the right components can quickly and efficiently re-establish vitamin levels, which is crucial when dealing with a brain injury. By providing vital fluids, IV therapy helps optimize the body's circulatory system, ensuring the organs receive sufficient oxygen.
Replacing fluid or blood loss due to wounds is an especially essential benefit of IV therapy for traumatic brain injury patients, who may have an imbalance of fluids or electrolytes and considerable blood loss. In particular, IV therapy is vital for stabilizing traumatic brain injury patients before any operative procedures.
IV therapy treatments that include specific fluids and vitamins can also benefit brain injury patients by improving cell and brain health. Specifically, IV therapies with B vitamins help lower homocysteine levels in the blood and slow brain shrinkage, which improves memory, energy levels and mood.
Recent research also indicates IV therapy may provide the benefits of neural stem cell therapy without introducing cells into brain injury patients. The treatment does so by using IV therapy to deliver neural exosomes — nervous system molecules that carry messages to the brain. Once inside the body, the exosomes work as mediators between other cells to improve brain function after a traumatic brain injury.
This new cell-to-cell messaging technology can help minimize or even stop a traumatic brain injury's progression by supporting cells following the injury and speeding neuron regeneration. As a less risky procedure, regenerative IV therapy would be preferable to invasive brain surgery. While further research is still necessary, this method has shown much promise for treating brain injuries so far.
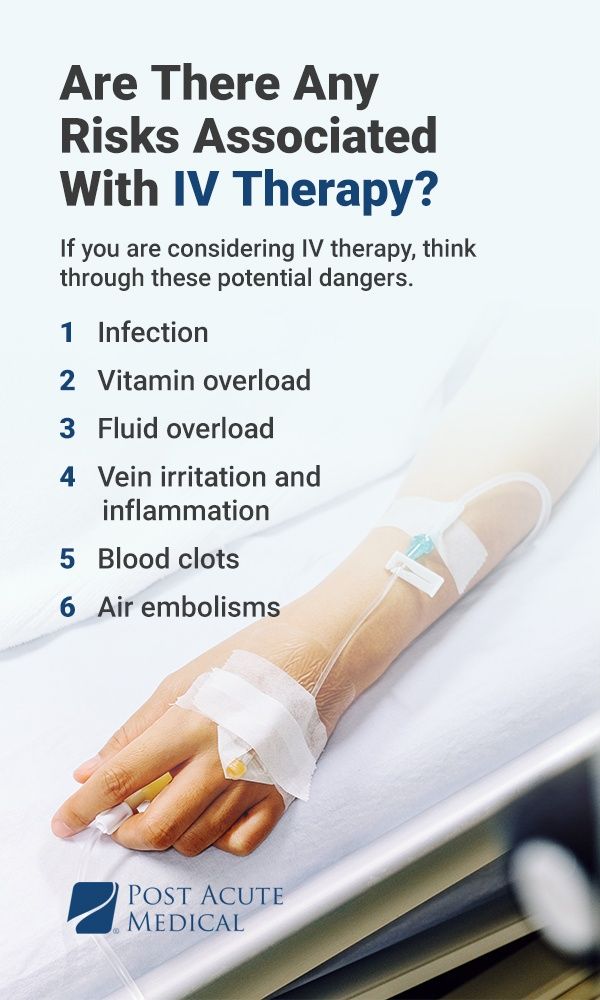
Are There Any Risks Associated With IV Therapy?
While IV therapy can be extremely beneficial for traumatic brain injury patients, you should be aware of the possible treatment risks. If you are considering IV therapy, think through these potential dangers.
- Infection: There is always a minor risk of sickness with IV therapy because inserting an IV creates a direct path to the bloodstream. In doing so, the IV treatment completely bypasses the body's first line of defense against bacteria — the skin. While the potential of developing an infection due to IV therapy is low, you must see a licensed medical professional for all IV therapy treatments to minimize the risk and ensure you receive a sterile, healthy infusion.
- Vitamin overload: With IV drip therapy, there is a danger of getting too much of a good thing. Receiving too much of some vitamins or minerals can increase the chances of adverse side effects such as organ damage. For example, the body stores an excess of a fat-soluble vitamin, such as vitamin A, where it might harm organs like the liver.
- Fluid overload: Just like vitamins, too many fluids can be bad for your health. If a health care professional does not adequately monitor the IV therapy treatment and the fluid drips too fast, the patient could experience an overload of fluids, which could throw off the body's electrolyte balance and damage the kidneys, heart and brain. Other symptoms of fluid overload include delayed wound healing, heart failure and impaired bowel function.
- Vein irritation and inflammation: Failure to find a suitable vein or poor IV insertion technique could result in a vein becoming irritated or inflamed. Because an IV drip treatment that does not get inserted properly can be quite painful, it is crucial to only visit a licensed medical professional for IV therapy.
- Blood clots: With more severe vein inflammation, a blood clot could form. A superficial blood clot could result in redness, tenderness and pain, plus more serious issues like limb pain or hardening of the affected vein. An untreated blood clot could lead to infection or more severe vein complications.
- Air embolisms: An IV line could introduce an air embolism, or a blockage of blood supply caused by small air bubbles in the heart or a blood vessel. Air embolisms could result in a stroke if not addressed quickly and correctly.
Though IV therapy comes with a few risks, working with a dependable medical facility to receive IV therapy treatments can help reduce the risk of anything going wrong during the procedure. When you visit a trustworthy health care facility like Post Acute Medical for IV therapy, you can rest assured you are getting top-quality care from a certified medical professional.

Schedule an Appointment With Post Acute Medical
If you are looking for a safe treatment center to receive brain injury therapy, schedule an appointment with Post Acute Medical today. At Post Acute Medical, we take quality care to another level by prioritizing patient satisfaction and long-term positive outcomes.
Our team of dedicated, compassionate staff will develop an individualized brain injury rehabilitation plan to treat your specific symptoms. Whether you need long-term care, inpatient or outpatient rehabilitation, Post Acute Medical offers a range of resources for helping brain injury patients make a full recovery.
To discuss the brain injury treatment programs available to you or to schedule an appointment, locate the Post Acute Medical facility nearest you.